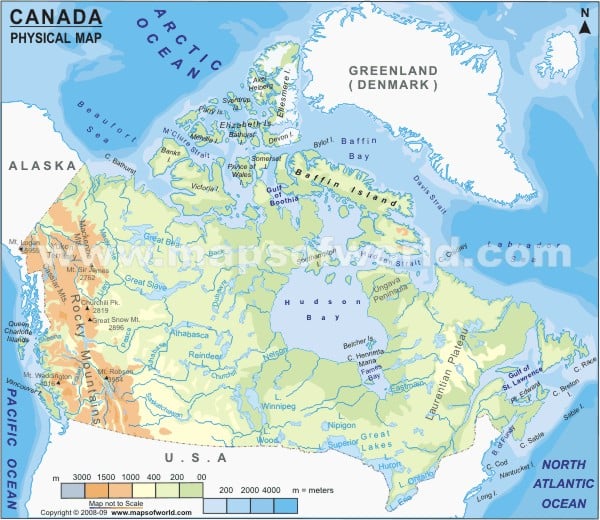
Canada is the world’s second-largest country located in North America. The country’s ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic to the Pacific and northward into the Arctic Ocean.
Canada Physical Features
The country covers a total area of 9.98 million square kilometres (3.85 million square miles). Canada shares its western and southern border with the United States and is the world’s longest bi-national land border (8891 kilometres (5,525 mi)).
The Vast Geography of Canada occupies parts of the continent of North America and has the Pacific Ocean in the east and west, and the Arctic Ocean to its north. The physical geography of the country is widely varied. A map legend at the bottom gives all the signs, characters, graphics, and symbols used throughout the map. The topography of Canada can be divided into:
Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountain runs through parts of southern Quebec in Canada. The ranges are named as Chic-Choc and Notre Dame. Long Range Mountains are a chain of mountains along the west coast of the Canadian island of Newfoundland. The ranges in the Appalachian Mountains include Mount Jacques-Cartier (1,268 m or 4160 ft) and Mount Carleton (817 m, 2680 ft).
Great Lakes and St.Lawrence Lowlands
The lowlands cover the southern parts of Quebec and Ontario, in the Great Lakes and st. Lawrence River Basin. The region is a rich sedimentary plain covering a flat land area between the Canadian Shield and the Appalachian Mountains.
Canadian Shield
The region is also called the Laurentia Plateau and is a large area of exposed Precambrian igneous rocks and high-grade metamorphic rocks. The site covers the northeastern part of Alberta, northern parts of Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Ontario, Quebec, Labrador and the Great Northern Peninsula of Newfoundland. The region consists of mainly eroded hilly terrain on a vast rock base. The area has many lakes and essential rivers in northern Quebec and
Ontario. Some of the regions of the Shield are referred to as mountain ranges, including Laurentian Mountains and the Torngat Mountains.
Canadian Interior Plains
The region is a vast sedimentary Plain that sustains extensive grain farming in the southern part of the province. The area covers prominent aspects of Alberta, Southwestern Manitoba, Southern Saskatchewan, and Taigs and Boreal region.
Canadian Arctic
The Canadian Arctic contains the northernmost mountain system in the world. The region comprises permafrost and tundra north of the treeline, encompassing geological areas such as the Arctic Cordillera and Arctic lowlands. The Arctic Cordillera includes the British Empire Range and Ellesmere Island.
Canadian Cordillera and the Canadian Rocky Mountains
The region includes the Coast Mountains in British Columbia, separating the Interior Plateau from the Pacific Ocean. The mountain range runs from the lower Fraser River and the Fraser Canyon northwestward. Canadian Rocky Mountain lies in the easternmost part of the Canadian Cordillera. These mountain ranges are bounded west by Rocky Mountain Trench, east by Canadian Prairies, and north by the Liard River. The Canadian Rockies have many high peaks, such as Mount Columbia (3,747 m 12,293 ft) and Mount Robson (3,954 m, 12973 ft).
The drainage system of Canada
The country holds vast reserves of water. Canada has at least 47 rivers of lengths 600 (230 sq mi) Square kilometres. The government has over 2,000,000 lakes, of which 563 lakes are greater than 100 Square kilometres. The most significant rivers of the country are the Mackenzie river and Saint Lawrence River and important lakes Great Slave lake, Great Lakes, Lake Nipigon and more.