About Bolivia
Explore this Bolivia map to learn everything you want to know about this country. Learn about Bolivia location on the world map, official symbol, flag, geography, climate, postal/area/zip codes, time zones, etc. Check out Bolivia history, significant states, provinces/districts, & cities, most popular travel destinations and attractions, the capital city’s location, facts and trivia, and many more.
| Official Name: | (Republic of Bolivia) Republic de Bolivia |
| Capital: | La Paz |
| Population: | 8.5 million |
| Area: | 1.09 million sq km or 0.42 million sq mi |
| Currency: | The Boliviano ($1=6.71) |
| Religion: | Christianity |
| Literacy: | 83% |
| Languages: | Spanish, Quechua and Aymara |
| Major Cities: | La Paz, Santa Cruz, Potosi |
| Climate: | Cold, dry climate in elevated areas while warm climate in low-lying areas |
Bolivia, a South American state, derives its name from famous South American freedom fighter, Simon Bolivar. Bolivia has been through many coups and after nearly 18 years of military rule finally restored independence in 1982.
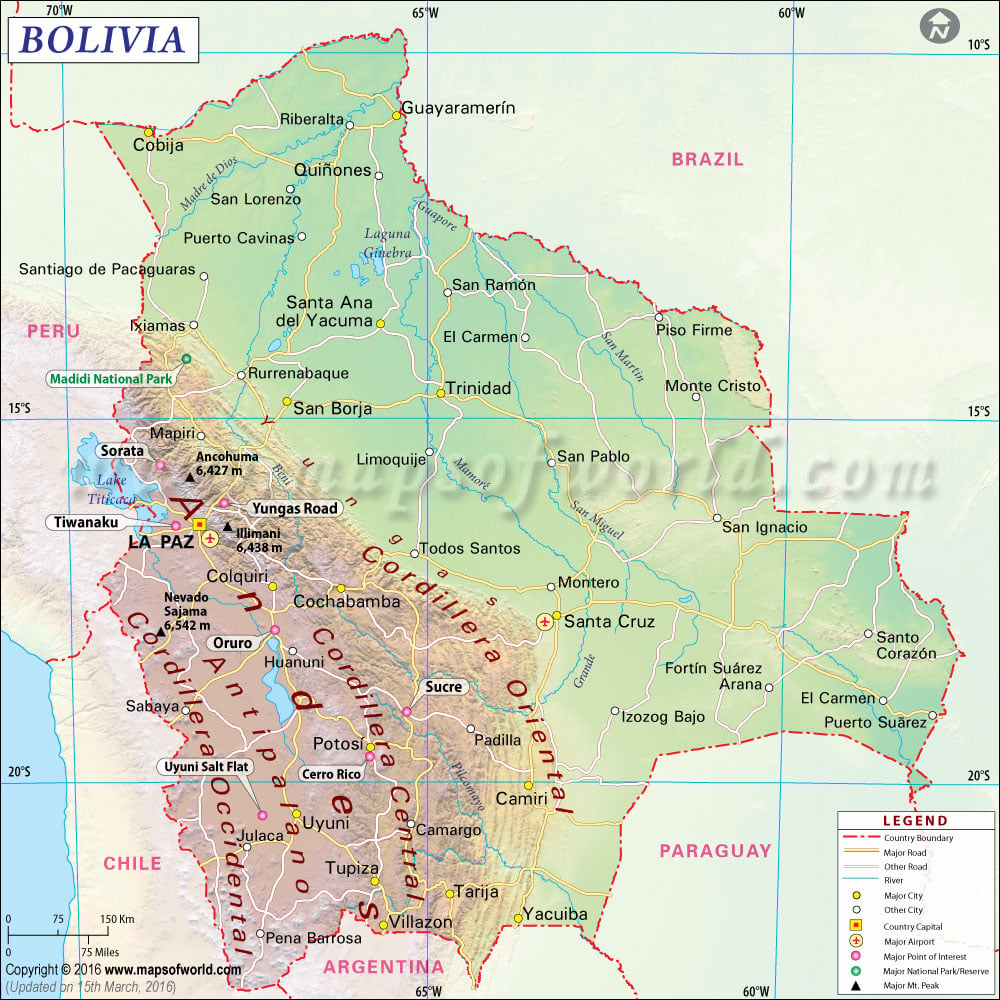
Physical Map of Bolivia
The main physical feature of Bolivia is the Andes mountain range, which extends from north to south, across the western part of the country.
The Andes form two ranges in Bolivia, the western range, the Cordillera Occidental that runs along the Chilean border; and the eastern range, the Cordillera Oriental, the main range, which crosses the west central part of Bolivia.
The Cordillera Oriental contains some of the highest Andean peaks, notably Ancohuma, Illampu and Illimani. The rivers that flow through Bolivia are the Beni and its main affluent, the Madre de Dios; the Guapore, which forms part of the boundary with Brazil; and the Mamore.
Flora And Fauna of Bolivia
Owing to wide variations in elevation, plant and animal species of nearly every climatic zone are found in Bolivia. The flora of Bolivia includes a coarse grass, called ichu, which is mainly grown on barren high plateau in the west. Other trees include para rubber trees, more than 2,000 species of hardwood trees, and vanilla, sarsaparilla, and saffron plants, which mainly grow in the tropical forests of the east. The fauna of Bolivia include the llama, found chiefly on the Altiplano which is used for carrying goods. Monkeys, pumas, jaguars, armadillos, and a variety of reptiles, birds, and insects are also found in Bolivia.
Location of Bolivia
Bolivia is bound on the north and east by Brazil, on the southeast by Paraguay, on the south by Argentina, and on the west by Chile and Peru.
Climate of Bolivia
The climate of Bolivia is mainly governed by its various elevations. While the higher regions experience cold and dry climate, the low-lying areas have warmer climate. The mean annual temperatures range from 8ºC to 26ºC.
People of Bolivia
The people of Bolivia are made up of roughly 55 percent of Native Americans and about 30 percent of mestizo who are a mixture of Native American and European race. The remaining 5 percent is made up of white people, mainly of Spanish descent. Most of the people live in urban areas, only around 37 percent live in rural areas.
Flag of Bolivia
The flag of Bolivia is made up of three equal horizontal bands – red at the top, yellow in the center and green at the bottom. The yellow band has the coat of arms in the center.
Economy of Bolivia
Though Bolivia has had a long spell of poor economy, this Latin American country is marching along the progress path to become a market-oriented economy.
Efforts in this direction included the signing of a free trade agreement with Mexico and becoming an associate member of the Southern Cone Common Market (Mercosur), as well as the privatization of the state airline, telephone company, railroad, electric power company, and oil company. However, in 1999, growth slowed as a result of the government budget policies, which limited needed appropriations for anti-poverty programs, and the fallout from the Asian financial crisis. In 2000, major civil disturbances held down overall growth to 2.5%. Bolivia’s GDP failed to grow in 2001 due to the global slowdown and a lack in domestic activity.

 Wall Maps
Wall Maps