About Benin
Explore this Benin map to learn everything you want to know about this country. Learn about Benin location on the world map, official symbol, flag, geography, climate, postal/area/zip codes, time zones, etc. Check out Benin history, significant states, provinces/districts, & cities, most popular travel destinations and attractions, the capital city’s location, facts and trivia, and many more.
| Official Name | Republic of Benin, Republique du Benin |
| Capital | Porto Novo |
| Population | 6.4 million |
| Area | 112,622 sq km or 43,483 sq mi |
| Currency | Franc CFA ($1=724.11) |
| Religion | Animism, Islam & Christianity |
| Literacy | 37% |
| Languages | French & Tribal dialects like Fon, Yoruba |
| Major Cities | Porto Novo, Cotonou, Parakau |
| Climate | Varies from equatorial type to tropical |
One of the smallest and most densely populated states of Africa, Benin was formerly one of the provinces of French West Africa, until it gained independence in 1960.
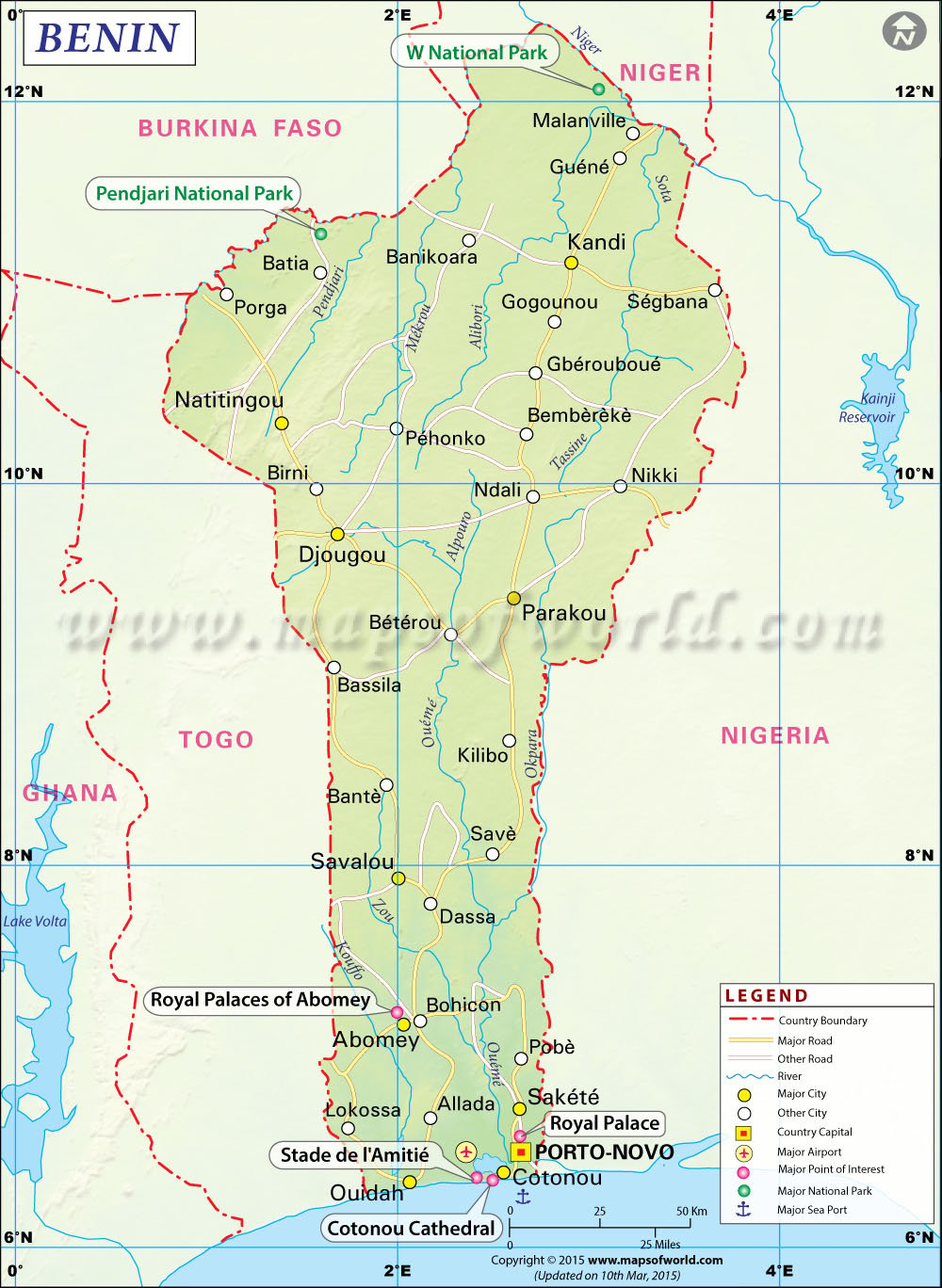
Physical Map of Benin
Along the coast, Benin has a sandy barrier beach with no natural harbors.
The northern side of the beach consists of shallow lagoons, and farther north is a fertile lowland, most of which is intensively cultivated.
In northern Benin, the land rises into a 1,600-ft high plateau of ancient rocks and mostly infertile soils and covers the rugged Atakora Mountains in the northwest.
The main rivers of northern Benin are the Niger, which forms part of the boundary with the republic of Niger, and its tributaries, the Sota, Mékrou, and Alibori.
Location of Benin
The country of Benin is bordered on the north by Burkina Faso and Niger, on the east by Nigeria, and on the west by Togo. Benin covers a total area of 112,622 sq km.
Flora And Fauna of Benin
Though dense tropical rain forests once covered much of the land behind Benin’s coastal strip, now the forests exist only in the areas near the rivers and palms form the principal tree of the region. Woodlands form a large part of central Benin, and grasslands are found in abundance in the drier north. Various animals found in Benin include elephants, buffalo, antelope, panthers, monkeys, crocodiles, and wild ducks.
Benin Information says that agriculture is the most important part of the economy of the country since it offers produces like cotton, palm oil, cassave, maize, cashew nuts, rice and fishing.
Flag of Benin
The flag of Benin is made up of two equal horizontal bands – yellow at the top and red with a vertical green band on the hoist side.
Climate of Benin
The climate of Benin ranges from equatorial type in the south to arid tropical wet-and-dry climate in the north. The south receives about 1,300 mm of rainfall a year, mainly from March to July and October to November. The average monthly temperature ranges from 20° to 34°C. The north experiences high temperatures and receives an annual rainfall of about 890 mm from May to September.
People of Benin
Most of the population of Benin lives in the rural areas, only about 43 percent live in urban areas. The entire population is made up of 42 ethnic groups, namely the Fon and the closely related Adja, which are the main ethnic groups who together make up about three-fifths of the population in the south.
In the north, the Bariba and Somba together account for about one-sixth of the population, while one-tenth of the population is made up of the Yoruba in the southeast. Though French is the official language, most of the people speak African language. In the north, Islam is practiced by 20 percent of the people while Christianity is practiced by 25 percent of the population.
Economy of Benin
The economy of Benin is mainly dependent on agriculture. In the past five years, Benin had managed to bring stability in real output, but growing population soon made it instable. Most of the enterprises in Benin were nationalized in the 1970s, but worsening economic conditions forced the government to sell most of them in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Now the government of Benin plans to attract more foreign investment, place more emphasis on tourism, facilitate the development of new food processing systems and agricultural products, and encourage new information and communication technology. The national budget in 1993 anticipated $272 million in revenues and $375 million in spending. In 2001 the gross domestic product (GDP) was $2.4 billion.