Australia, known as the Commonwealth of Australia, officially comprises the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania and many smaller islands.
Physical Features of Australia
Australia covers a total area of 7,617,930 square kilometres (2,941,300 sq mi) and is the largest country in Oceania. Surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the south pacific ocean and the Pacific Ocean, Australia has often been termed an “Island Continent”. The Coastline of mainland Australia is 35,821 km (22,258), with an additional island coastline of 23,860 km (14,830 mi).
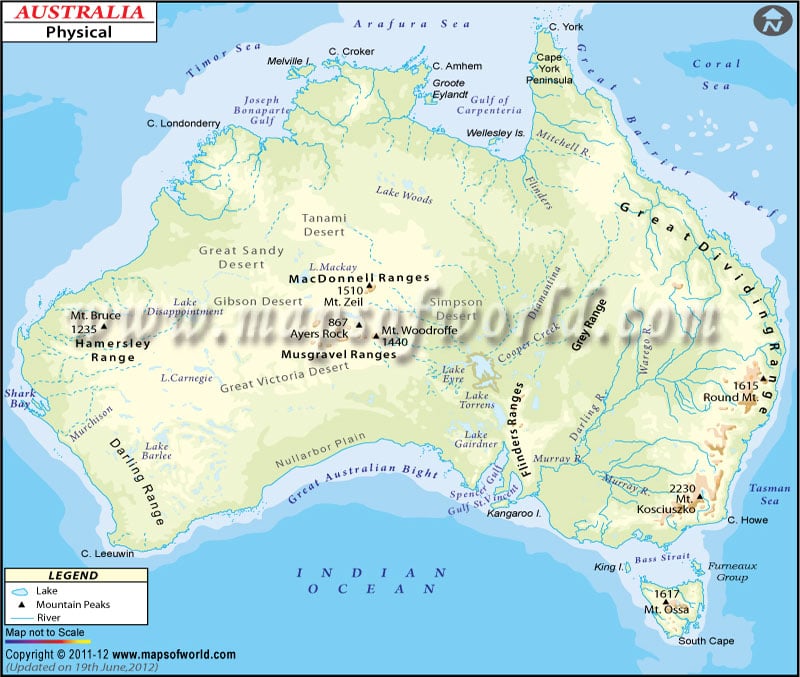
A map legend at the bottom gives all the signs, characters, graphics, and symbols used throughout the map. The Australia Physical Map can be used for school work, presentation and other purposes. The land of Australia is a megadiverse exhibiting incredible biodiversity and a variety of landscapes with deserts in the centre, tropical rainforest in the northeast and mountain ranges in the southeast. Some of the essential topographic features of Australia:
Western Plateau
The region covers two-thirds of the continent, including large parts of Western Australia, Northern Territory and South Australia. The area rises to mountain elevation near the west coast and falls to lower heights near the continental centre. The plateau region is mainly flat and arid though broken by mountain ranges such as MacDonnell Ranges, Hamersley Range and Musgrave Range.
Great Dividing Range
The Great Dividing Range or Eastern highlands lies near the eastern coast of Australia. The region consists of an extensive combined complex of mountain ranges, Plateaus and rolling hills. These ranges run parallel to the east coast of Australia, roughly separating the eastern coastal plain from the rest of the continent. The range stretches from Dauan Island in Torres Strait, running the entire length of the eastern coastline through New South Wales and fading into Wimmers plains. The content is more than 3500 kilometres (2175 mi) and varies in width (160km-300km). The highest peak of Australia, Mount Kosciuszko, lies in snowy mountains, part of the Great Dividing Range.
Central lowlands
The Central Lowlands region lies between the Eastern Highlands and Western Plateau. The area comprises the Great Artesian Basin and Australia’s most extensive river system, Lake Eyre Basin and Murray-Darling Basin. Murray-Darling Basin is a vast geographical area in the interior of southeastern Australia. The basin spans most of New South Wales, Victoria, parts of Queensland and South Australia. On the other hand, lake Eyre Basin is the largest endorheic basin, including much of inland Queensland, a part of western New South Wales, parts of South Australia and Northern Territory.
Uplands of Central Australia
The region is a deserted and xeric shrublands ecoregion of Australia. Prominent features include Great Victoria Desert, Uluru, Great Sandy, Gibson, Nullarbor Plain on the southern coast and more.
Great Barrier Reef
The region is the world’s most extensive coral reef system, extending over 2,000 km (1,200 mi). It is composed of over 2,900 individual reefs and 900 islands. The reef is located off Queensland, Australia, in the coral sea.
Important Rivers and Lakes in Australia
One of the most significant rivers in Australia, the Murray River is the longest in the country. The tributary of Murray River includes Darling, Murrumbidgee, Paro and Warrego River. The significant rivers of western and northern Australia include Ashburton, Murchison and Victoria.