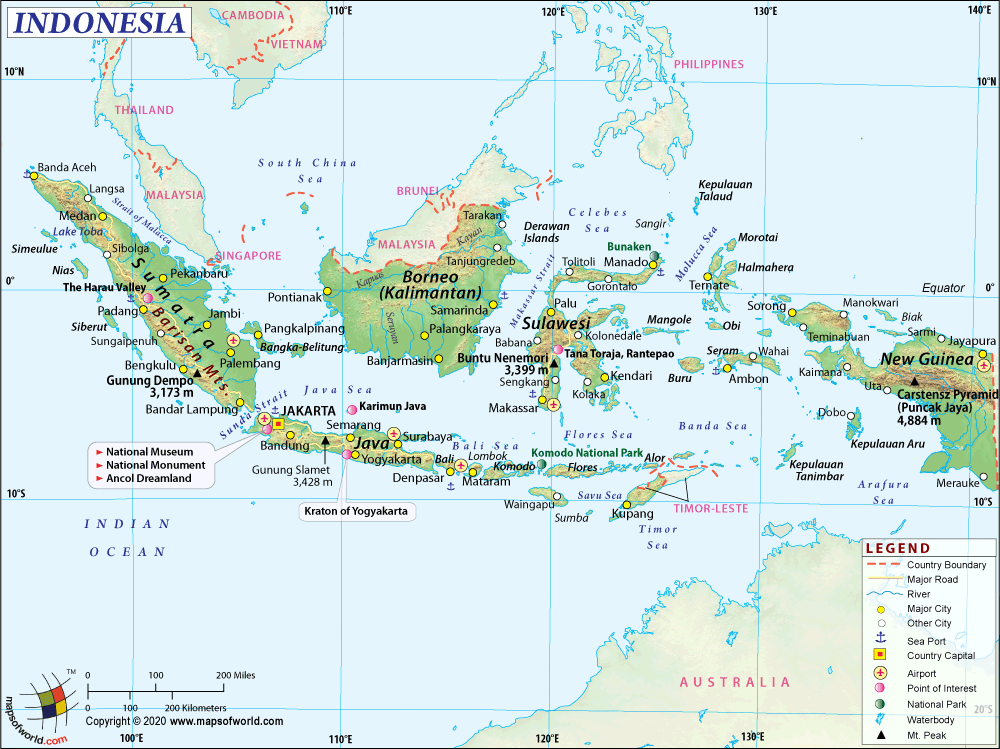
Map of Indonesia
- Indonesia Provinces - Aceh, Bali, Bangka-Belitung, Banten, Bengkulu, Gorontalo, Jakarta Raya, Jambi, Jawa Barat, Jawa Tengah, Jawa Timur, Kalimantan Barat, Kalimantan Selatan, Kalimantan Tengah, Kalimantan Timur, Kalimantan Utara, Kepulauan Riau, Lampung, Maluku Utara, Maluku, Nusa Tenggara Barat, Nusa Tenggara Timur, Papua, Riau, Sulawesi Barat, Sulawesi Selatan, Sulawesi Tengah, Sulawesi Tenggara, Sulawesi Utara, Sumatera Barat, Sumatera Selatan, Sumatera Utara, West Papua, Yogyakarta
- Neighboring Countries - Singapore, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, Australia
- Continent And Regions - Asia Map
- Other Indonesia Maps - Where is Indonesia, Indonesia Blank Map, Indonesia Road Map, Indonesia Rail Map, Indonesia River Map, Indonesia Cities Map, Indonesia Political Map, Indonesia Physical Map, Indonesia Flag
Explore this Indonesia map to learn everything you want to know about this country. Learn about Indonesia’s location on the world map, official symbol, seal, flag, geography, climate, postal/area/zip codes, time zones, etc. Check out Indonesia’s history, significant states, provinces/districts, & cities, most popular travel destinations and attractions, the capital city’s location, facts and trivia, Top FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions), and many more.
About Indonesia
Indonesia (officially the Republic of Indonesia) is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. The country is considered transcontinental, where its territory consists of islands geologically considered as part of either Asia or Australia. The country lies between the Indian and the Pacific Oceans and consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of New Guinea and Borneo. Indonesia is the world’s largest Archipelagic state extending 1760 kilometers (1094 mi) from north to south and 5120 kilometers (3181) from east to west. The country consists of thousands of distinct native ethnic and hundreds of linguistic groups, with Javanese being the largest. To learn more about Indonesia, check out Key facts of Indonesia.
Indonesia Flag
The flag of Indonesia was introduced in 1945 on August 17 during the proclamation of Independence in Jakarta at 56 Proklamasi Street. It was hoisted in public on December 27, 1949, when the Dutch formally transferred sovereignty. The design of the Indonesian flag is a simple bicolor flag with two equal horizontal bands with red on top and white on the bottom with an overall ratio of 2:3. The official name of the flag is Sang Saka Merah Putih, and the red color in flag symbolizes courage. In contrast, white is the symbol of purity.
The national emblem of Indonesia is Garuda Pancasila representing an eagle bird with a heraldic shield on its chest, and a scroll gripped by its legs.
Indonesia Location
The Indonesia Location Map shows the exact location of Indonesia on the world map. This map shows the boundaries of this country, neighboring countries, and oceans. The archipelagic country is located in southeast Asia, lying between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. The location of Indonesia is strategic along major sea lines connecting East Asia, South Asia, and Oceania.
The Latitude and Longitude extent of Indonesia is 11.S and 6. N Latitude and 95. E and 141. E Longitude in Asia. One can check this Latitude and Longitude Map of Indonesia for more information.
Indonesia Capital
The capital city of Indonesia is Jakarta at present. The city is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in Southeast Asia. Jakarta has served as the capital of Indonesia since the time of Independence. Due to ongoing environmental concerns and deteriorating Air pollution levels, the island country’s government has decided to shift the capital from Jakarta to Nusantara. Nusantara is located in East Kalimantan, an Indonesian Province on the Island of Borneo, about 2000 km (1250 miles) northeast of Jakarta.
Indonesia Time Zone
Indonesia geographically stretches across four time zones, from UTC+06:00 in Aceh to UTC+09:00 in Papua. However, the government of Indonesia recognizes only three time zones in its territory, which are:
- Western Indonesia Time (WIB) is seven hours ahead of the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) that is ( UTC+07:00).
- Central Indonesia Time (WITA) is eight hours ahead of UTC (UTC+08:00)
- Eastern Indonesia Time (WIT) is nine hours ahead (UTC+09:00).
Indonesia Geography
The physical map of Indonesia reveals all the details about the country’s physical features, including mountain peaks, rivers, and lakes. The archipelagic country has about 13,466 islands, according to the geospatial survey conducted between 2007 and 2010 by National Coordinating Agency for survey and mapping (Bakosurtanal). According to the Indonesian government of Indonesia, 8,844 are named islands, of which 922 are permanent. The five main islands of the country are Sumatra, Java, Borneo (Kalimantan), Sulawesi, and New Guinea. There are two major island groups: Nusa Tenggara and the Maluku Islands, and sixty smaller island groups. Four islands of Indonesia are shared with other countries: Borneo island is shared with Malaysia and Brunei, New Guinea is shared with Papua New Guinea, Sebatik in Kalimantan, and Timor is shared with East Timor.
Indonesia Climate
The climatic conditions of Indonesia tend to be relatively even year-round as the country lies along the equator. The country mainly has two seasons, the wet and dry seasons, with no extremes of summer and winter. The dry season of Indonesia falls between May and October, and the wet season is between November and April. The climate of Indonesia is dominated by the tropical rainforest climate (Af) found on every large island in Indonesia. The oceanic climate prevails in the highland areas adjacent to the rainforest climates with uniform precipitation. The southeastern part of Indonesia is predominantly tropical savanna (Aw).
Indonesia History
The history of Indonesia dates back as early as 1.9 million years ago. Archaeological evidence suggests that ancestors of modern human-occupied sites in Central and East Java at that time. The first formal kingdom (Srivijya) flourished around A.D 550-1050. The domain was the Buddhist trading polity, whose power-centered region of present-day Palembang. Later the empire of Majapahit centered in east java. Islam entered the archipelago in the 11 century, but the significant conversation lasted only two or more centuries.
Western visitors began to appear in the archipelago in the late thirteen century. It started with Marco Polo and continued with the Portuguese and Spanish in the sixteenth century. In 1596 Dutch visited the region, and Dutch power grew very gradually. In the first few decades of the twentieth century, the Dutch colonial state extended its control to the region we now call Indonesia.
In 1945 on August 17, Sukarno (a well-known nationalist figure) and Mohammad Hatta proclaimed the Independent Republic of Indonesia with Sukarno as president. Finally, in 1949 on December 27, the Federal Republic of the United States of Indonesia was formally recognized, which a year later was formed into the unitary Republic of Indonesia. Power was transferred from Sukarno to a high-ranking army officer Suharto. In 1967 on March 12, Suharto became the acting president, and the New Order era began in Indonesia.
Indonesia Major Cities
The Indonesia Cities Map reveals valuable details, including the capital city and administrative divisions. Major cities of Indonesia are:
Provinces in Indonesia
The country is divided into thirty-seven provinces ( administrative divisions), the local government’s highest tier. They are formerly called first-level region provinces (Provinsi Daerah Tingkat |). The provinces in Indonesia are further divided into regencies and cities ( formerly called second-level region regencies and cities or Kabupaten/kotamadya Daerah Tingkat II). These are further divided into districts (Kecamatan). Check this Indonesia Provinces Map to locate all the provinces of Indonesia on the map. The provinces in Indonesia are grouped into seven geographical units for statistical and national planning purposes. Below are the maps of the provinces of Indonesia :
- Aceh Province Map
- Bali Provinces Map
- Bangka Belitung Province Map
- Banten Province Map
- Bengkulu Province Map
- Gorontalo Province Map
- Jakarta Raya Province Map
- Jambi Province Map
- Jawa Barat Province Map
- Jawa Tengah Province Map
- Jawa Timur Province Map
- Kalimantan Province Barat
- Kalimantan Selatan Province Map
- Kalimantan Tengah Province Map
- Kaliimantan Timur Province Map
- Kalimantan Utara Province Map
- Kepulauan Riau Province Map
- Lampung Province Map
- Maluku Province Map
- Maluku Utara Province Map
- Nusa Tenggara Barat Province Map
- Nusa Tenggara Timur Province Map
- Papua Province Map
- Riau Province Map
- Sulawesi Barat Province Map
- Sulawesi Selatan Province Map
- Sulawesi Tengah Province Map
- Sulawesi Tenggara Province Map
- Sulawesi Utara Povince Map
- Sumatera Barat Province Map
- Sumatera Selatan Province Map
- Sumatera Utara Province Map
- West Papua Province Map
- Yogyakarta Province Map
Indonesia Airports
Indonesia has about 683 Airports as of 2013. The airports in Indonesia range from significant international airports to modest unpaved airports on remote islands and inland interiors throughout the archipelago. Most of the airports in Indonesia are operated by Transportation Ministry technical operation units and state-owned PT Angkasa Pura I & II. Check Indonesia Airports Map to locate all the airports on the Map. The main and the busiest airport in Indonesia are:
- Jakarta International Airport (Soekarno-Hatta International Airport)
- Ngurah Rai (Bali) International Airport
- Juanda International Airport
- Hasanuddin International Airport
- Sentani International Airport
- Blimbingsari (Banyuwangi Airport)
Indonesia Postal Codes
Postal codes in Indonesia consist of five digits. In the local language, postal codes are known as Kode pos. The first digits represent the region in which a given post office falls. The second and third digit represents the regency (Kabupaten) or city (Kota), and the fourth digit indicates the district (kecamatan) within Kabupaten or Kota. The final digit indicates the commune or village or Kelurahan/desa. There is an exception for Jakarta postal codes as the third digit indicates the district (Kecamatan), and the fourth digit indicates the urban village (kelurahan).
Indonesia Travel
Indonesia is one of the most popular travel destinations in Southeast Asia. Tourism in Indonesia is an integral part of the Indonesian economy. In 2017 country was ranked 20th in the world tourism industry and third-fastest tourist industry growth in Asia and the fastest in Southeast Asia. Some of the well-known tourist attractions of Indonesia are:
Top FAQs on Indonesia
FAQ #1: Is Indonesia in India?
Ans: Indonesia is not in India. It is an island country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and the Pacific Oceans.
Faq #2: How many islands are in Indonesia?
Ans: There are approximately 17,508 islands in Indonesia.
Faq #3: Is Bali in Indonesia?
Ans: Bali is an Island and a province of Indonesia in the westernmost of the lesser Sunda Islands.
Faq #4: Is Indonesia a democracy?
And:4 Indonesia is a democratic country with the framework of a presidential representative democratic republic. The president of Indonesia is both head of the state and head of government and has a multi-party system.
Faq #5: What religion is Indonesia?
And: Indonesia is a secular-multi faith country and officially recognizes six religions. These religions are Islam, Buddhism, Protestantism, Hinduism, Catholicism, and Confucianism,
Faq #6: What is Indonesia’s type of government?
Ans: Indonesia is a presidential representative democratic republic.
Faq #7: What is Indonesia known for?
Ans: Indonesia is known for its various landmarks, magical waterfalls, Hindu temples, and some of the most active volcanoes in the world.
Faq#8: How big is Indonesia?
Ans: Indonesia has an area of 1.905 million km2.
Faq#9: What language is spoken in Indonesia?
Ans: Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian) is the official and primary language of Indonesia.
 Wall Maps
Wall Maps