Bahrain Map
- Bahrain Cities - Manama
- Neighboring Countries - Qatar, United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Iran
- Continent And Regions - Asia Map
- Other Bahrain Maps - Where is Bahrain, Bahrain Blank Map, Bahrain Road Map, Bahrain Political Map, Bahrain Flag
About Bahrain
Explore this Bahrain map to learn everything you want to know about this country. Learn about Bahrain location on the world map, official symbol, flag, geography, climate, postal/area/zip codes, time zones, etc. Check out Bahrain history, significant states, provinces/districts, & cities, most popular travel destinations and attractions, the capital city’s location, facts and trivia, and many more.
| Official Name | The Kingdom of Bahrain (Mamlakat al-Bahrayn) |
| Capital | Manama |
| Population | 1,248,348 (2011 estimate) |
| Area | 727 sq. km or 274 sq. mi |
| Currency | Bahraini Dinar (BHD) |
| Country Code | 973 |
| Time Zone | Atlantic Standard Time Zone (UTC/GMT +3) |
| Literacy | 94.60% |
| Languages | Standard Arabic (official), English, Kerinci, Korean, Malayalam, Northern Kurdish, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu, Western Farsi. |
| Major Cities | Manama, Al-Muharraq, Ar-Rifa, Dar Kulayb, Madinat Hamad |
| Climate | Arid climate, very hot summers and mild winters |
| Major Religions | Islam (80% Shia) |
An Arab state, Bahrain comprises of 33 islands in the Arabian Gulf. Bahrain is the biggest of the islands and has lent its name to the entire archipelago.
Bahrain, in the west of Persian Gulf is formed by a union of 33 islands, divided into 5 governorates. It is headed by King Hamad bin Isa Al-Khalifa. It is connected with Saudi Arabia by King Fahd Causeway about 15 miles long. Bahrain has an arid climate characterized by extremely hot summers and mild winters. Irrespective of the differences in season the temperatures are mostly uniform in the country.
History
Bahrain has a rich history beginning with the Sumerians, Assyrians, Babylonians, Parthians, and going up to the British dominance of the region. Dilmun in ancient Bahrain was a trade center between Mesopotamia and the Indus Valley Civilization. Under Alexander, the Great it served as the center of pearl trading. It remained under Achaemenid control from the 6th century BC to the 3rd century BC. After them the Parthians, Sassanids followed in succession. After the 7th century AD Bahrain was ruled by representatives of Prophet Mohammed. They were succeeded by the Qarmatians. They were conquered by Uyunids who ruled from 1076 to 1235. Portuguese occupied Bahrain in 1521 for 80 years to be followed by Safavid ruler Shah Abbas I. The Safavids were defeated by Omani rulers who ruled Bahrain till it was recaptured by Nadir Shah of Persia in 1730 with the aid of British and Dutch. Political strife continued till the Al-Khalifas were formally declared the rulers of Bahrain by the British. Oil was discovered by the Bahrain Petroleum Company in 1932. Bahrain participated in World War II and sided with the Allies. It finally became independent in August 15, 1971.
Sports
The people in Bahrain actively engage in sporting activities such as football, basketball, handball, horse racing, rugby, and volleyball. Bahrain has participated in six summer Olympics but has not won any medal till date. It has never competed in any of the winter Olympics. The country conducts the Bahraini Premier League in September featuring top ten football clubs of the country. The professional basketball league has eleven clubs in it. The Formula One race-track of Bahrain hosts major racing events since its inception in 2004. Kayaking and scuba diving are popular sports.
Government
Bahrain is a constitutional monarchy headed by King Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa. It gained independence from United Kingdom on August 15, 1971. Bahrain formally adopted its Constitution on February 14, 2002. The Constitution of Bahrain permits three organs of government. Despite universal suffrage the power is largely vested with the royal house and its members.
Executive:
The Executive is headed by the King together with the Council of Ministers. The Council of Ministers is directly appointed by the King. Bahrain has had only one Prime Minister since 1971, Khalifa ibn Sulman Al Khalifa. The Crown Prince Salman bin Hamad Al Khalifa is the supreme commander of Bahraini armed forces.
Legislative:
The Legislature is led by the King and the National Assembly. The National Assembly is bicameral with two houses. The lower house is called the Chamber of Deputies and the upper house is called the Shura Council. The members of the lower house are elected democratically through universal suffrage whereas the upper house is constituted by the members elected by the King.
Judiciary:
The Judiciary is classified into two branches – the Civil Law Courts and the Shari’a Law Courts. All commercial, criminal, and civil cases fall under the purview of the former while the latter concerns itself with all matters pertaining to Muslims in the country. The judges of the lower and middle courts are appointed by the Ministry of Justice on the advice of the Prime Minister. The King chairs the Supreme Judicial Council.
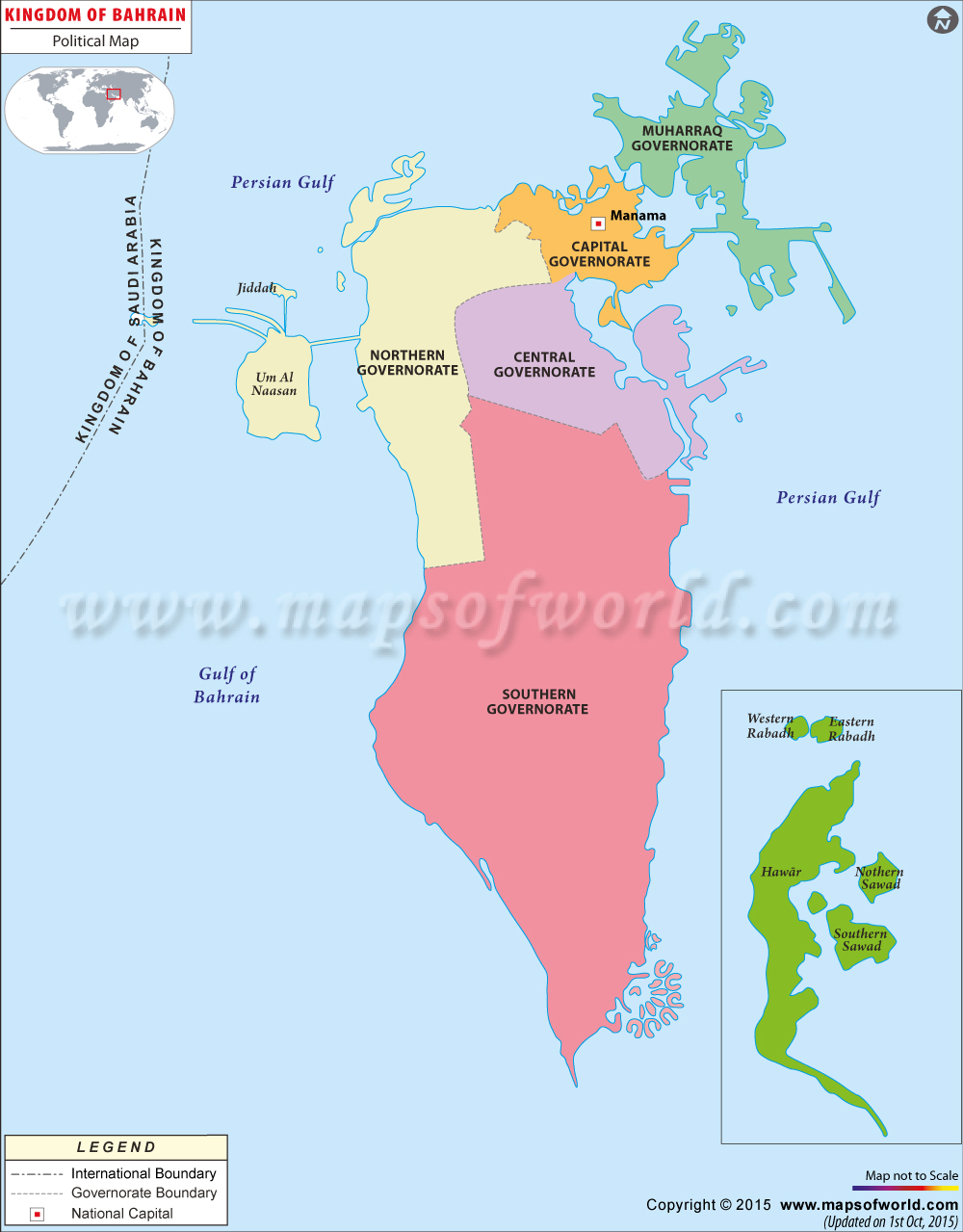
Bahrain is divided into five governorates – Asamah Governorate, Janubiyah Governorate, Muharraq Governorate, Shamaliyah Governorate, and Wasat Governorate each administered by a governor and the municipal council.
Law and Order
After the institution of constitutional monarchy there have been instances of frequent protests against the government. Iran has been active in promoting civil unrest in the region. However bilateral talks with all political parties have been undertaken to address this political and civil unrest. Demonstrations are usually curbed with a heavy hand leading to indiscriminate arrests and detentions. Measures are, however, underway to promote harmony in the region.
National Holidays and Festivals:
Being an Islamic state Bahrain celebrates all festivals of the Islamic lunar calendar including Eid-al-Fitr, Eid-al- Adha, the Islamic New Year, Mouloud, and Ashura. Bahrain celebrates National Day on December 16 to commemorate the coronation of the former king Isa bin Salman Al Khalifa. In addition to these, Christmas, New Year’s Day, and Labour Day are official holidays. The country allows all ethnic communities to observe festivals of their group without any hindrance.
Location of Bahrain
Bahrain lies 24 km east of Saudi Arabia and 29 km west of Qatar.
Climate of Bahrain
The summers are extremely hot and humid in Bahrain, especially between April and October, with temperatures regularly rising to 43° C and sometimes reaching 52° C. However, winters are more pleasant with temperatures plummeting to 20° C or below. Seasonal winds periodically cause sandstorms and rough seas.
Flora And Fauna of Bahrain
Bahrain is home to a variety of plants and animals. Most of the plants that are found in Bahrain are salt-tolerant and desert resistant types, out of which palm trees are quite common. Animals include snakes and other reptiles, hares, scorpions, hedgehogs, and gazelles while the marine life is made up of mackerels, shrimps, pearl oysters, and dugongs.
Flag of Bahrain
The flag of Bahrain is red with a white serrated band, consisting of five white points on the hoist side. The five points represent the five pillars of Islam.
Bahrain lacks dramatic topographical features, such as mountains or valleys. The main island consists of a low desert plain that rises to a low central escarpment where Bahrain’s highest point, Jabal ad Dukhan (134 m/440 ft), is located. Bahrain also lacks rivers, lakes and water bodies and obtains water for drinking and irrigation from underground aquifers. The smaller islands are generally low-lying, some being only a few feet above sea level.
People of Bahrain
The estimated population of Bahrain in 2011 is 214,705 of which 235,108 are from foreign nations such as India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Britain, Philippines and other gulf nations. 80% of the people are Muslims but the nation is known to be tolerant towards all religions. The ethnic groups in the country include Bahraini Arabs, Iranians, Indo-Pakistanis, Filipinos, and British. It also has a small Jewish population.
Culture and Society:
Bahrain being a predominantly Muslim country, all actions are dictated by the Sunnah. Family forms the fundamental unit of society and is highly respected. Nepotism is not viewed negatively as it is believed to inspire trust. Women are granted universal suffrage and hold important positions in all important professions. Women are expected to dress modestly on all occasions. High level of etiquette is expected to be observed at all times to prevent offending local customs and traditions.
Arts and Entertainment:
Bahrain has a seamless blending of Islamic and modern cultures. Bahrain is known for publishing the most number of books in the Arab world. Bahrain has produced popular musicians like Ali Bahar and Khalid Al Shaikh. Bahrain has modern musical institutes like Bahrain Music Institute, Bahrain Orchestra, and Classical institute of Music. It is the hub of Khaleeji and Sawt music. The modern age has brought with it progressive rock and heavy metal. Bahrain houses the La Fontaine Center of Contemporary Art, Al Riwaq Art Gallery, Albareh Art Gallery to promote indigenous and contemporary art of Bahrain.
Economy of Bahrain
With an annual GDP of $30.8 billion and a real growth rate of 1.5%, Bahrain is the tenth freest economy in the world. It tops the list in Middle East and North Africa region. According to the United Nations Economic and Social Commission (ECOSOC) for Western Asia it is the fastest growing economy of the Middle East. It has a high per capita income $27300 but 10.8% of the labor force is unemployed.
Petroleum and natural gas contribute 60% to the annual export revenues and add 30% to GDP, forming the spine of the economy. Crude oil resources being scarce, Bahrain, in collaboration with Kuwait, United States, and Saudi Arabia also undertakes crude oil processing and natural gas liquefaction. After oil, aluminum is the biggest export product of the country.
Bahrain is a prime hub of Islamic finance. To further the diversification process Bahrain has largely privatized utilities like telecommunications, financial services, and banks, after signing the US-Bahrain Free Trade Agreement. In the last decade tourism has grown by 156% in terms of revenue in Bahrain with the country witnessing an 81% increase of foreign tourists.
The agriculture is largely undeveloped due to lack of arable land and adds only 1% to GDP. The main export items of Bahrain include petroleum and allied products, aluminum, and textiles.
The government controls the oil and gas industry, most heavy manufacturing, and the bulk of the transportation and communications sectors, but it has undertaken efforts to privatize the economy, thus transferring banking, light manufacturing, and commerce into private hands.
Bahrain’s gross domestic product (GDP) was $7.9 billion in 2001. Services, including public administration, banking, and tourism, accounted for 59 percent of the GDP. Industry accounted for 40 percent, with manufacturing responsible for 19 percent and oil and gas extraction for most of the remainder. Agriculture contributed only 1 percent of the GDP.